Line detection is widely used in many robotic tasks such as scene recognition, 3D reconstruction, and simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). Compared to points, lines can provide both low-level and high-level geometrical information for downstream tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel edge-based line detection algorithm, AirLine, which can be applied to various tasks. In contrast to existing learnable endpoint-based methods which are sensitive to the geometrical condition of environments, AirLine can extract line segments directly from edges, resulting in a better generalization ability for unseen environments. Also to balance efficiency and accuracy, we introduce a region-grow algorithm and local edge voting scheme for line parameterization. To the best of our knowledge, AirLine is one of the first learnable edge-based line detection methods. Our extensive experiments show that it retains state-of-the-art-level precision yet with a 3-80 times runtime acceleration compared to other learning-based methods, which is critical for low-power robots.
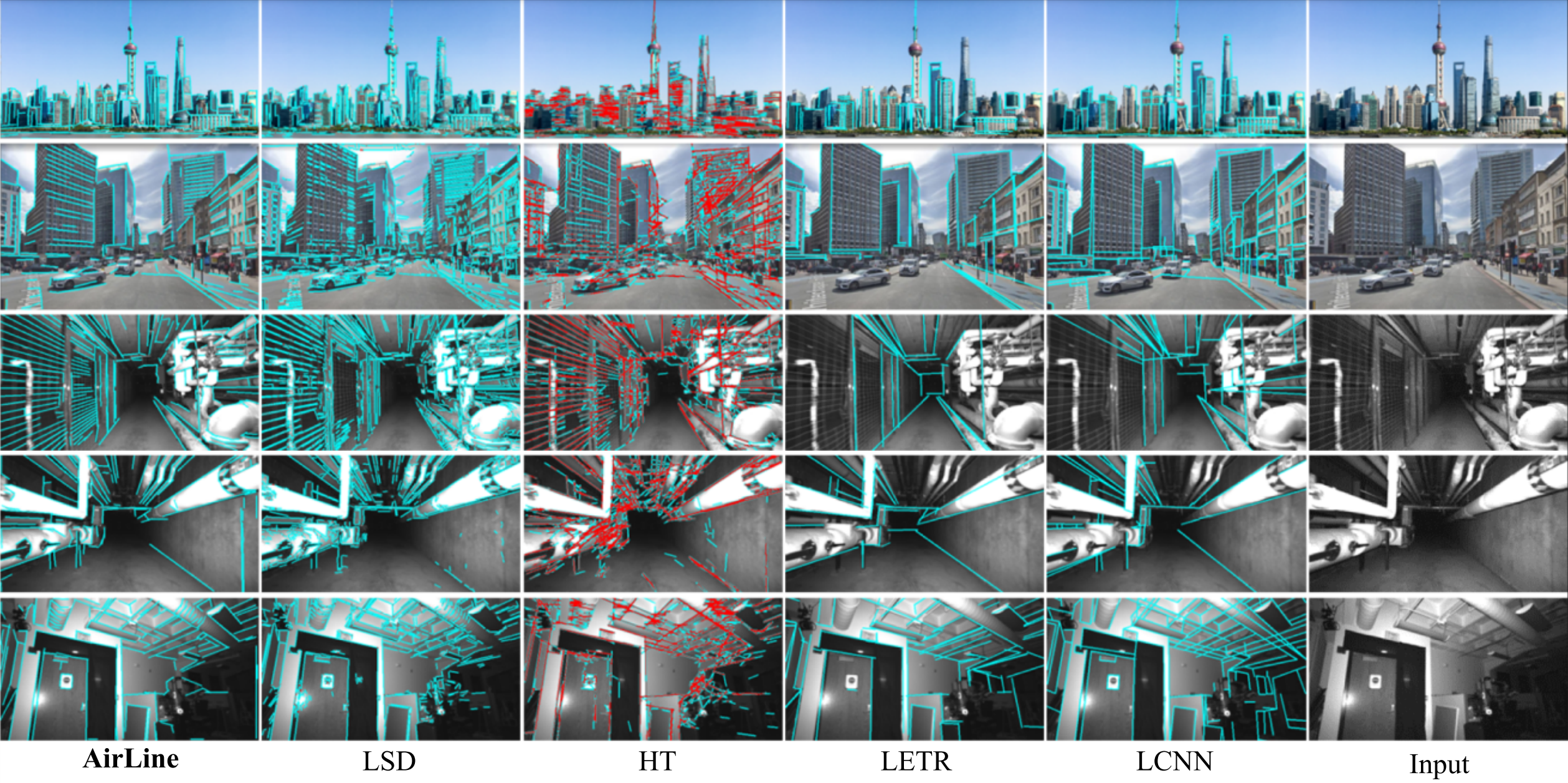

The following video clip demonstrates a qualitative comparison across difference methods on untrained sequence from UMA_VI. We found that the AirLine and LSD methods performed better than the LETR and LCNN in generating detailed line detections. Moreover, AirLine is preferred over LSD since it is able to merge the two sides of thin lines, while LSD tends to detect both sides. Though LCNN produces lines of high precision, it is not suitable for tasks that require detailed line inputs, as it tends to ignore short lines and connect two unrelated endpoints in complex environments. LETR, which performed the best under the endpoint precision mentioned in its original paper, was found to have the worst line quality in terms of precision, stability, and reasonable geometry.

Methodology
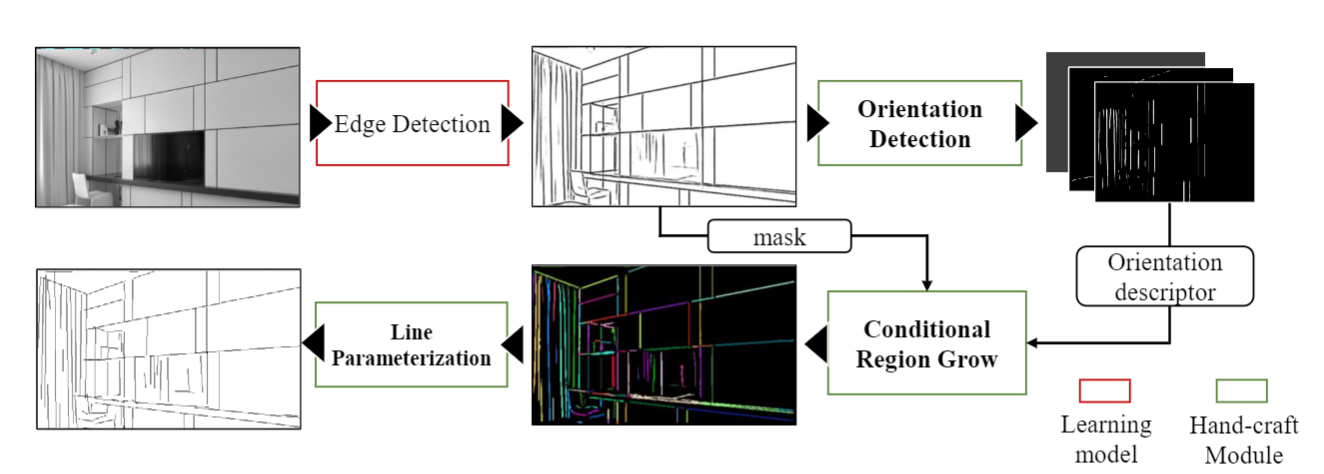
As shown above, AirLine is a learnable edge-based line detection architecture that is composed of four modules including edge detection, orientation detection, conditional region-grow, and line parameterization. We next present their motivation and detailed process, respectively. We made a video to demonstrate each stage.

By using edge-based learnable line detection approaches, AirLine has achieved state-of-art-level precision and significant efficiency and runtime boost.
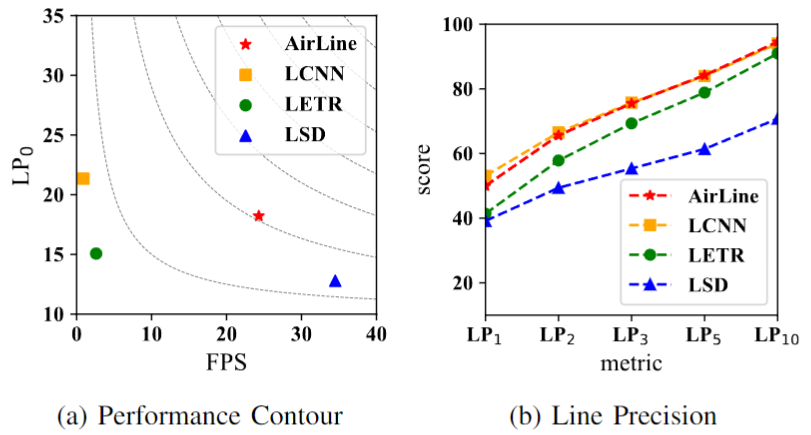
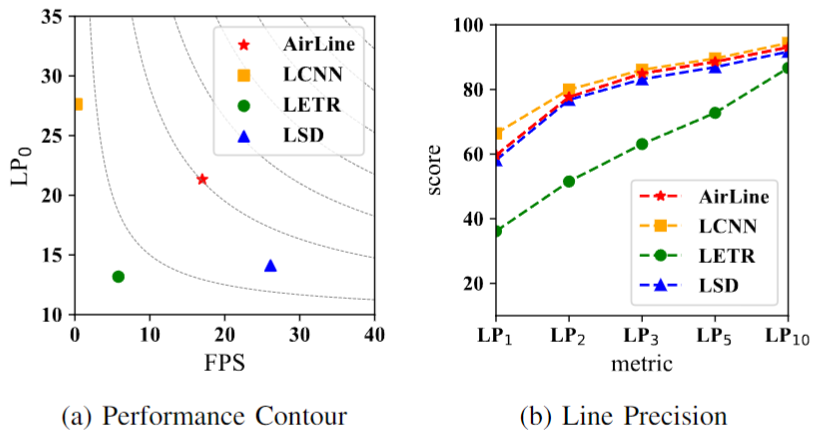
Publications
-
AirLine: Efficient Learnable Line Detection with Local Edge Voting.IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 3270–3277, 2023.


