Object encoding and identification is crucial for many robotic tasks such as autonomous exploration and semantic relocalization. Existing works heavily rely on the tracking of detected objects but have difficulty to recall revisited objects precisely. In this work, we propose a novel object encoding method, AirCode, based on a graph of key-points. To be robust to the number of key-points detected, we propose a feature sparse encoding and object dense encoding method to ensure that each key-point can only affect a small part of the object descriptors, leading it to be robust to viewpoint changes, scaling, occlusion, and even object deformation.
Object Representation
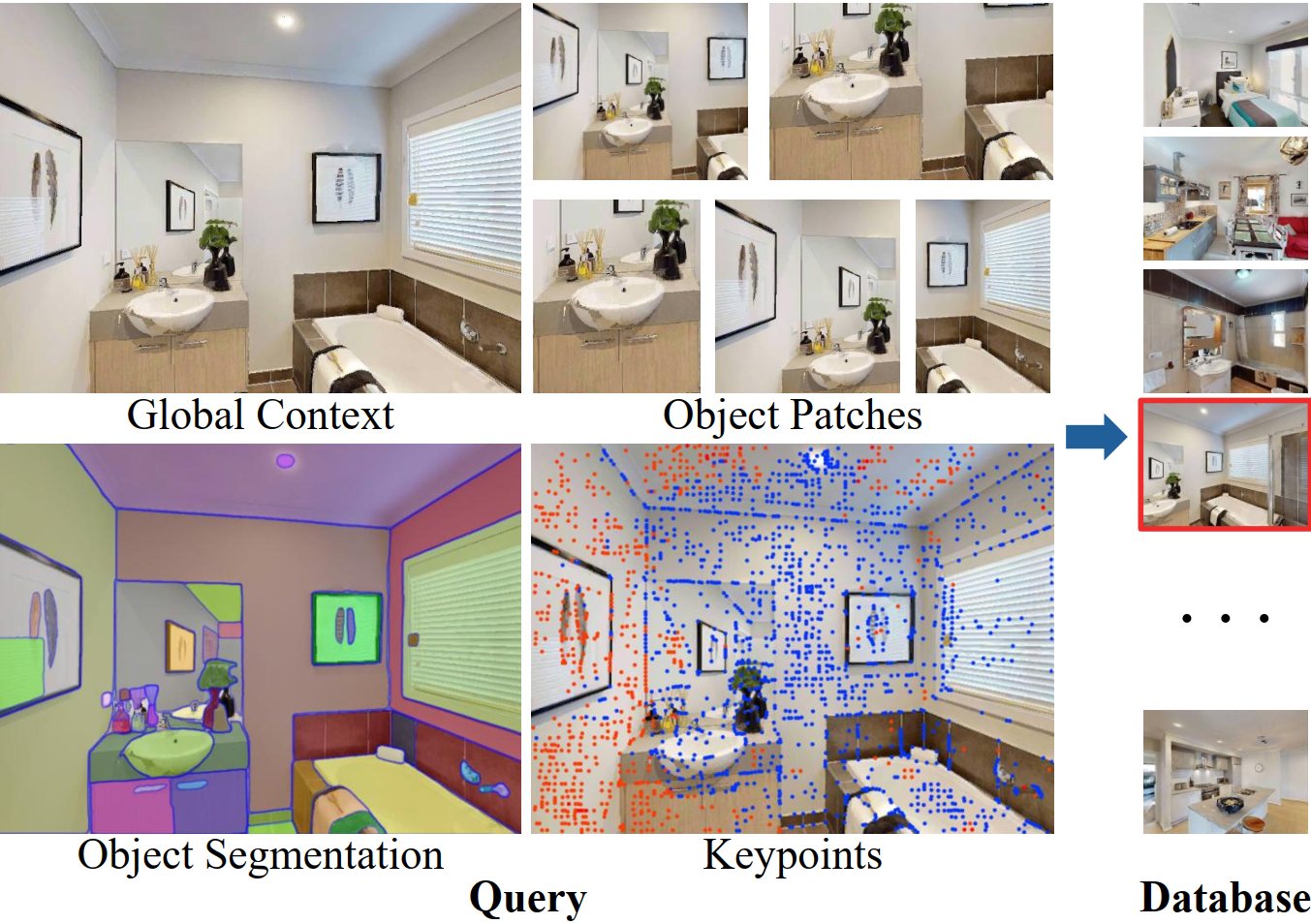
To save computational resources, object matching in SLAM is often based on key-point features, as the feature-based SLAM methods are still widely used. Inspired by the recent progresses in deep learning-based key-point detector and feature matching methods, it becomes intuitive to encode an object via a group of key-points in an end-to-end manner, where the key-points on the same object form a graph neural network. Therefore, we can take the graph embeddings as the object descriptors.
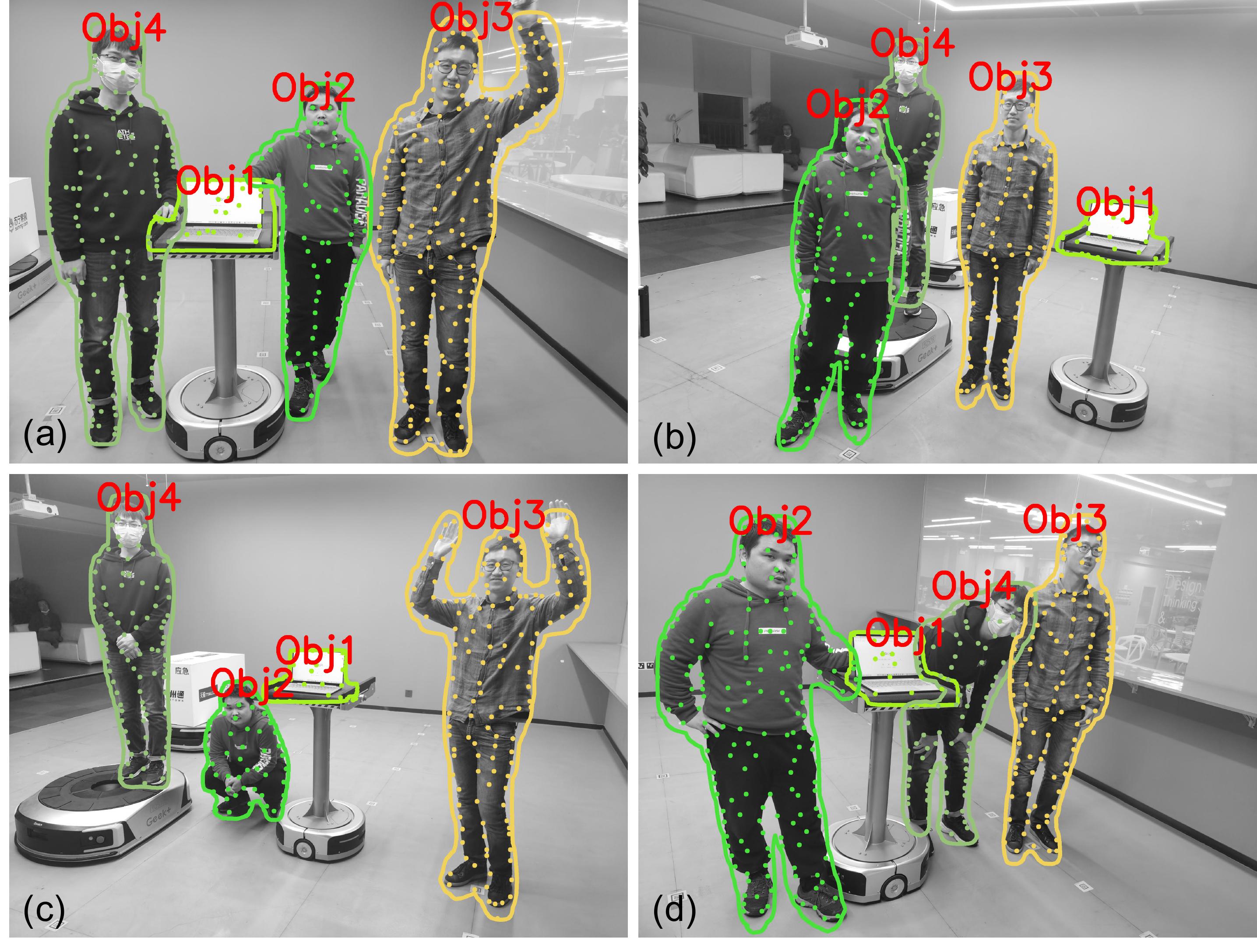

During robot exploration, robots often observe part of the objects due to occlusion and different viewpoints, resulting in that the object key-points only have a small overlap across different frames. Therefore, the key-points graph embedding will be easily affected, which makes it difficult to directly apply a graph network. To solve this problem, we argue that a key-point descriptor should have a sparse effect on the object embedding. This means that only a few positions of an object descriptor can be affected if a key-point is added or removed from an object graph. To achieve this, we propose a sparse object encoding method, which is robust to the change of viewpoint and object deformation.

Video
Publications
-
AirCode: A Robust Object Encoding Method.IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), 2022.